Introduction
In the dynamic landscape of Research and Development (R&D), organizations strive to optimize their productivity and achieve remarkable results. To accomplish this, it’s crucial to adopt data-driven practices and metrics that provide valuable insights into the development process. One such methodology gaining prominence is the use of DORA metrics, which stands for DevOps Research and Assessment.
This blog post will delve into the significance of DORA metrics and how they can be effectively utilized to enhance the productivity of an R&D group consisting of 70 individuals. By understanding the key metrics and implementing them in a thoughtful manner, organizations can foster a culture of continuous improvement and achieve outstanding outcomes.
What is DORA?
DORA is the acronym for the DevOps Research and Assessment group: they’ve surveyed more than 50,000 technical professionals worldwide to better understand how the technical practices, cultural norms, and management approach affect organizational performance.
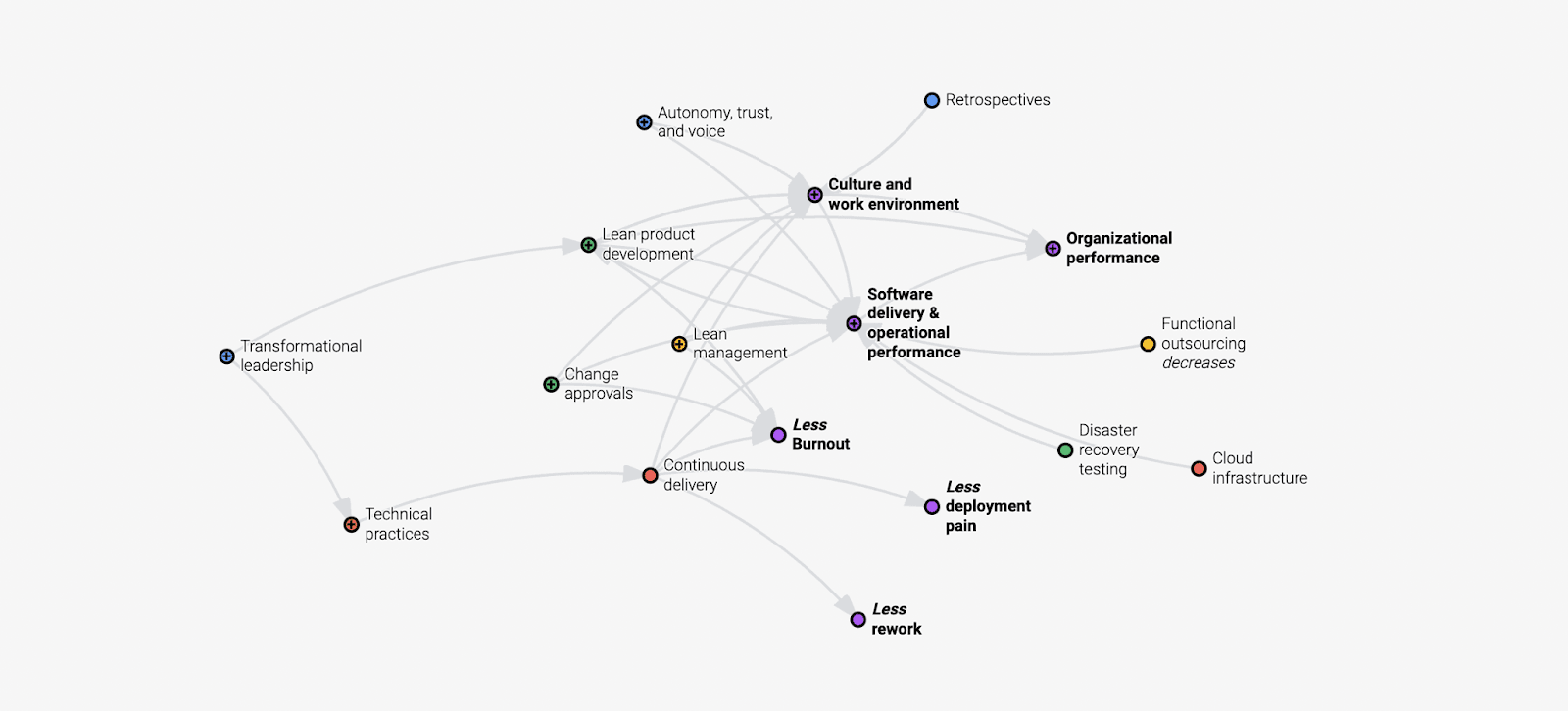
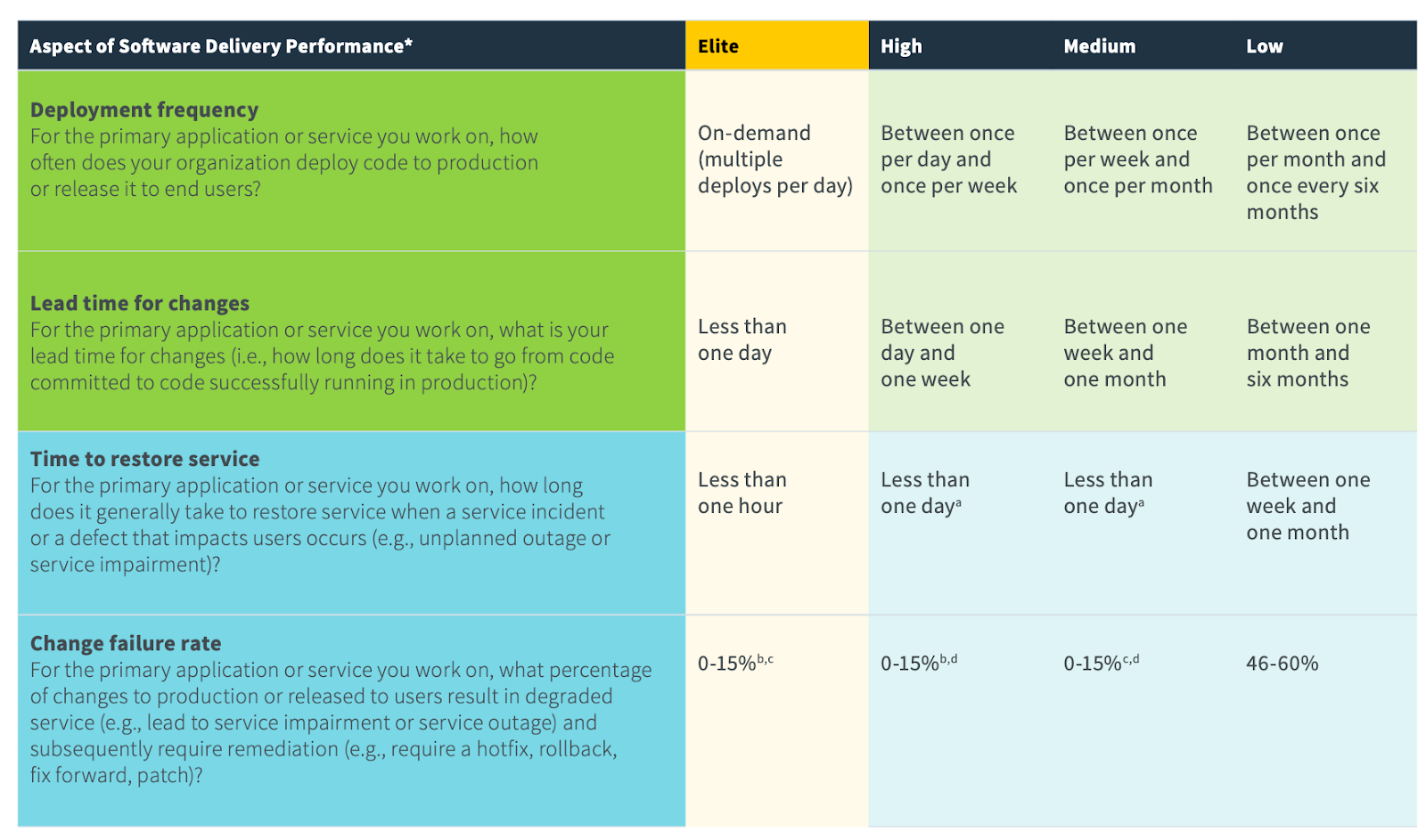
The four key metrics we measure
- Deployment Frequency — How often an organization successfully releases to production
- Lead Time for Changes — The amount of time it takes a commit to get into production
- Change Failure Rate — The percentage of deployments causing a failure in production
- Time to Restore Service — How long it takes an organization to recover from a failure in production
How do we understand the metrics?
- Deployment Frequency - limiting amount of code going to * production at once (limited batch size)
- Lead Time for Changes - reducing amount of blockers for developers
- Time to Restore Service - improving speed of incident recovery
- Change Failure Rate - improving quality focus
Following the rules of lean:
- Value is only released to production, once it leaves the factory floor (production deploy frequency)
- Optimize Work In Progress (lead time)
- Invest in SRE/automation (mean time to recover)
- Practice kaizen (change fail rate)
- Have efficient knowledge sharing and work allocation processes (time to onboard)
Get into business
To effectively utilize DORA metrics within an R&D group of 70 people, organizations should consider the following steps:
- Establish a Baseline: Begin by measuring the current performance of the R&D group across the DORA metrics. This provides a starting point for improvement and helps set realistic goals.
- Define Objectives: Identify specific objectives that align with the organization’s overall goals and strategies. These objectives should be measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART goals). For example, aim to increase deployment frequency by 20% within the next quarter.
- Foster a Culture of Learning: Encourage a culture of continuous learning and improvement within the R&D group. Create opportunities for knowledge sharing, experimentation, and innovation. Emphasize the importance of feedback and celebrate successes.
- Monitor Progress: Regularly track and analyze the DORA metrics to evaluate the progress towards the defined objectives. Use visual dashboards and reports to make the data easily accessible and understandable for the entire team. Iterate and Adjust: Based on the insights gained from the D